Most of us love sweets, and in one way or another, we have all been warned about their impact on our teeth. Food and beverage sugars are a major factor in the development of dental caries. The bacteria that cause plaque consume the sugar as an energy source, and as a waste product, they emit acid, which progressively erodes the enamel on the teeth. But how dangerous is sugar, and what kind of food should we cut to minimise the risk of damaging our teeth?
What are the effects of sugar on teeth?
Foods and drinks we consume enter our body through the mouth. Many health organisations and institutions have done studies that show that bacteria produce acid every time they encounter sugar in your mouth. So we can say sugar is like a magnet that pulls these harmful bacteria. And every time we consume food that contains sugar, our mouth gets flooded with more and more acid. What does this acid do? Easy; it consumes all your teeth.
Saliva is in charge of handling all the acid in our mouth, but as long as we continue getting sugar from our foods, there will be more acid produced. And there comes a point when saliva cannot handle all the acid, resulting in the loss of minerals from the enamel. After the protective layer, enamel, is destroyed, cavities are formed.

How do cavities develop?
Above, we explained that the main cause of cavities is sugar from foods and drinks. But let’s dive more into the process of cavity development.
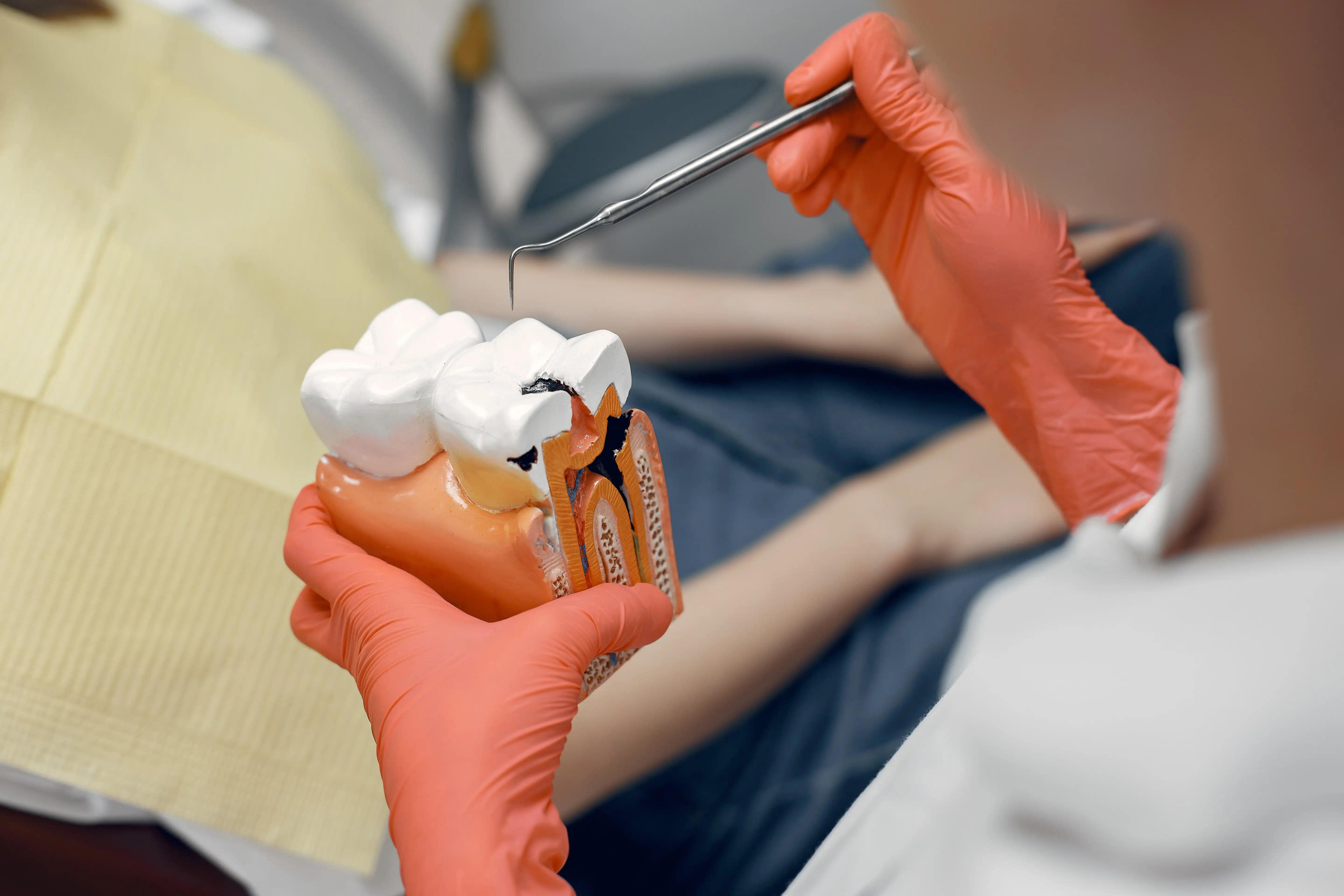
Tooth decay, also known as cavities, is the formation of holes because the enamel is damaged. It is caused by the presence of plaque in the mouth. Plaque is built from bacteria. It adheres to the teeth, and after some time, the acid released consumes the shiny and protective layer of enamel. This is called the first stage of cavities.
After this layer is damaged, it is easier for bacteria to reach the next layer of the tooth, dentin. Since dentin is softer and less resistant to acid, the teeth get more sensitive too. But it doesn’t end like this.
If no measures are taken, the damage is going to continue down to the most inner parts of the tooth, also known as the pulp. This part contains nerves and blood vessels, and the swollen pulp will press the nerve, causing pain. There are cases where the infection touches the bone or the other teeth nearby.
How does your mouth fight cavities?
The main defender of our teeth is fluoride. It is a chemical ion found in fluorine, a negatively charged substance. At the moment it meets a positively charged ion, it results in the creation of cavity fighters. But how does all this work?
We are already familiar with enamel, which is made from calcium and phosphate. In our mouth, there is saliva, which also contains calcium and phosphate and provides teeth protection. When sugar gets inside the mouth and acid gets reproduced, both phosphate and calcium get stripped from the enamel. In this case, fluoride comes in handy. Mostly taken from toothpaste or water, it gets combined with calcium and phosphate found in saliva to create the needed defence to protect our teeth.
What dental services can treat cavities?
There are some different procedures that dentists follow to treat cavities. Patients get treatment based on the stage of their tooth damage. For minor damage caused by cavities, you will be prescribed a specific toothpaste or mouthwash to restore enamel. Then the treatments continue to change for other stages. Dentists will suggest fillings and root canal treatment, and in extreme cases, you will have to extract the infected tooth.